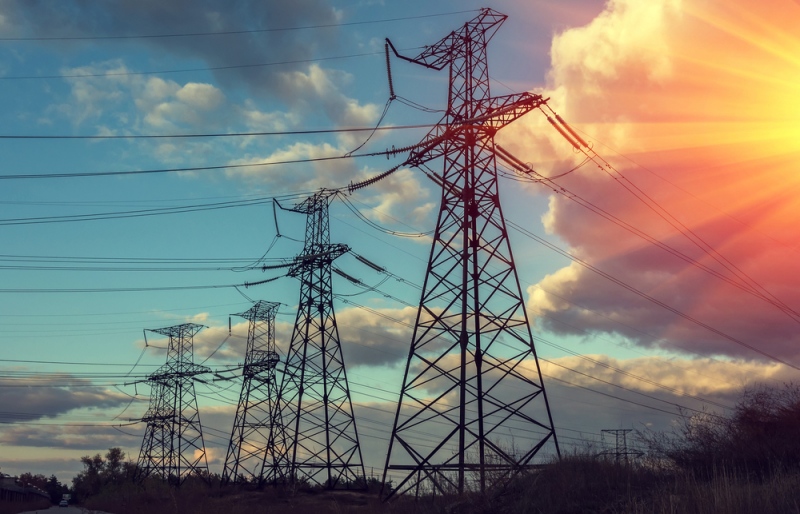
Whether it’s flicking the lights on and off or charging your phone, the power going into our homes and businesses is a resource that we somewhat take for granted. The reality is that there’s a huge mechanical and logistical operation in place from the National Grid that keeps electricity flowing.
Here we take a closer look at this and get to the bottom of what exactly the National Grid is and how it all works.
What is the National Grid?
To summarise, the National Grid is essentially a huge high-voltage electrical transmission network that covers the whole of the UK. This network joins power stations to substations around the country via pylons and cables which then connect to homes and buildings feeding our power supplies and electrical goods.
What does the National Grid do?
Beyond just ensuring that we have power in our homes, the Grid is used to make sure that there’s a constant source of electricity going to all parts of the UK. Power can essentially be redistributed around when certain locations have outages or low supplies.
How does the National Grid work?
The way the National Grid actually creates power from fossil fuels can be summed up in this five-step process:
#1 Fossil fuels are mined and brought to power stations.
#2 This is then burned to heat and boil vats of water to produce steam.
#3 This steam then rises from these vats and is directed in chambers housing turbines to drive these.
#4 The turbines start to spin which produces electricity – you can find out more about the specific workings of this here.
#5 The electricity that is created is then sent into transformers which are used to create the required voltage for the National Grid before it is distributed across the network.
Will the National Grid change in the future?
Back in 2008 new targets for carbon reductions to help fight climate change were introduced and ever since then the National Grid has been evolving to incorporate and use more sustainable sources of energy.
This includes wind farms, tidal energy and solar energy – and what’s more a number of coal and gas providers have since been shut down and are scheduled to close in efforts to make the grid more reliable on these cleaner energy resources.
So, the next time you’re turning on the power spare a thought for the impressive facilities and infrastructure that helps to make our lives easier and more convenient.